Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic lift systems are tools used to lower or raise work platforms and other surfaces unable to be moved by manual labor. They are powered by liquid mechanics via the combination of a hydraulic cylinder and hydraulic fluid.
Quick links to Hydraulic Lifts Information
Hydraulic Lift Applications
Hydraulic lifts are a crucial category of industrial plant and facility equipment, whether you are transporting within a manufacturing plant, mezzanine, construction site, warehouse, transportation facility, or shipping business. Their major applications are loading and unloading, resource relocation, accessibility, and warehouse maintenance.
- Loading and Unloading
- Made to perform safe and repeated operations, these weight lifting tools can lift and place items wherever they need to go as desired by the operator. You can perform loading and unloading as many times as you want. Hydraulic lifts replace the need for manual lifting and moving.
- Resource Relocation
- Hydraulic lifts are also used for moving workers from one place or level to another. Within construction and manufacturing sites lacking staircases or ones which have multiple stories, hydraulic lifts can be leveraged for timely and safe transportation of workers.
- Accessibility
- Hydraulic lifts provide immediate access to spaces otherwise difficult to reach. On-site technicians often require timely access to a remote or high location and hydraulic lifts can transport workers to these areas to perform maintenance tasks.
- Warehouse Maintenance
- For warehouses, custom hydraulic lifts can speed up the progress of operations. With a lift, warehouse maintenance becomes effortless. Whether it is the inspection of the warehouse or the loading and unloading of goods and materials, every maintenance exercise becomes stress-free and quick.
- The manufacturing industry is a major utilizer of hydraulic lifts, especially in warehouses requiring both personnel lifts (like scissor lifts) and material handling lifts (such as pallet lifts). However, many other industries use hydraulic lifts as well, particularly construction (during roofing and masonry work), automotive and transportation (during vehicle repairs and inspections), docking, and shipping. Additionally, lifts are used in aviation as passenger and luggage elevators. Hydraulic lifts are even used in private residential contexts to improve handicap accessibility.
History of Hydraulic Lifts
Humans have been using lifts for about as long as they have been constructing tall buildings. For instance, the Romans used platforms that lifted when slaves pulled at the ropes. Hydraulics, however, did not come into the picture until much later.
Joseph Bramah patented the first piece of hydraulic equipment, the hydraulic press, in England. This invention revolutionized agriculture and, eventually, all the industrial world. Across Europe, hydraulic power was used to power trains, elevators, canal locks, rotating sections of bridges, and cranes.
A slew of different inventors in the 19th and 20th centuries worked to create better, stronger, and more versatile lifts. In its early years, though, the hydraulic lift was primarily used with the elevator. Elevator lifts still exist today. Sir William Armstrong invented the hydraulic crane, used in lifting applications, in 1846. The first hydraulic elevator lift in the United States was installed in 1870 in New York. It replaced earlier lifts, which were powered by steam from burning coal.
Peter Lunati patented the first completely hydraulic automotive lift in 1925. By the 1940s, there were many lift manufacturers out there, so a group of American manufacturers came together to form a standards organization: ALI (Automotive Lift Institute).
The next big lift type, the scissor lift, was patented as recently as 1963 by Charles L. Larson. The 1960s also saw other lift innovations, such as the design of the sidelifter by Kaspar Klaus of Germany. In the 1980s, engineers combined technologies to patent a scissor-type hydraulic car lift. In 2000, manufacturers came out with a four-post hydraulic vehicle platform lift. Today, the hydraulic lift industry is as full of innovation as ever. Though the equipment already present in the industry works, engineers continue to make lifts stronger, better, and easier to use.
How Hydraulic Lifts Work
All types of hydraulic lifts are powered the same way. Based on the principle of hydraulics, hydraulic lifts utilize force that is applied to a hydraulic fluid to transfer energy from one area to another.
During this process, the force is multiplied, making hydraulics a powerful movement generation method. The transferred energy drives the hydraulic cylinder within the lift, which then provides the required energy to raise or lower an object.
Hydraulic Lift Images, Diagrams and Visual Concepts
 hydraulic lift, a device for moving objects using force created by pressure on liquid inside a cylinder that moves a piston upward.
hydraulic lift, a device for moving objects using force created by pressure on liquid inside a cylinder that moves a piston upward.
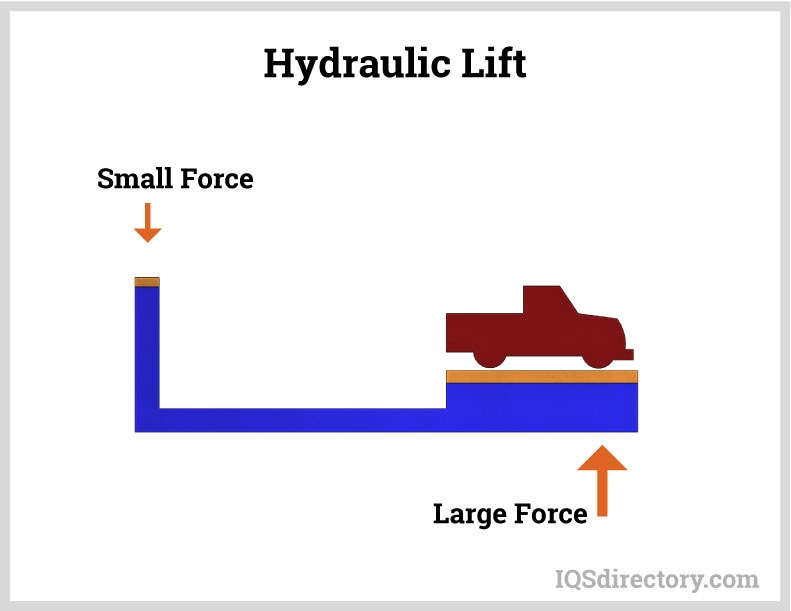 The principle of a hydraulic lift is by transfering the pressure to all points of the fluid.
The principle of a hydraulic lift is by transfering the pressure to all points of the fluid.
 Hydraulic fluids transfers power in the hydraulic system and is mostly mineral oil or water.
Hydraulic fluids transfers power in the hydraulic system and is mostly mineral oil or water.
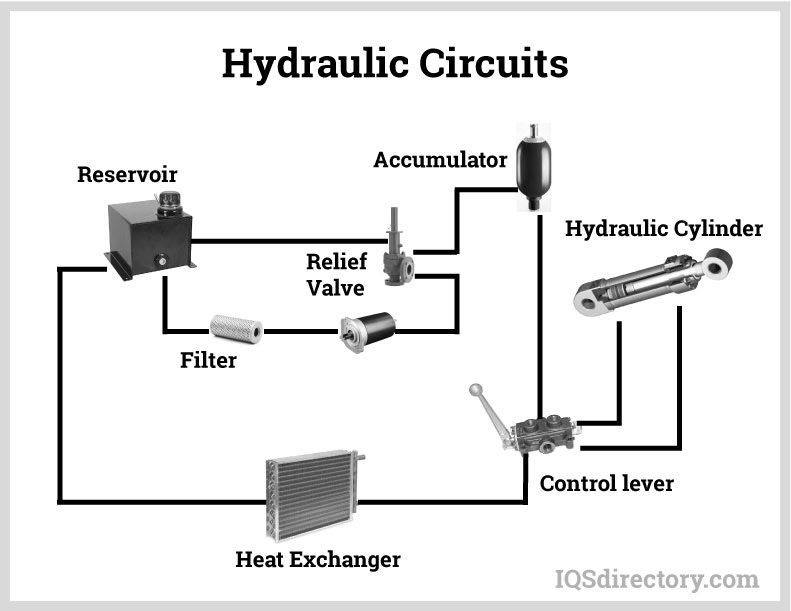 Hydraulic Circuits control the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid.
Hydraulic Circuits control the flow and pressure of hydraulic fluid.
 Personnel lifts, an example of electric hydraulic lift.
Personnel lifts, an example of electric hydraulic lift.
 Manual pumped lifts are raised by a manual hydraulic hand pump which makes them very sturdy and maintenance free.
Manual pumped lifts are raised by a manual hydraulic hand pump which makes them very sturdy and maintenance free.
Notable Types of Hydraulic Lifts
To accommodate the many applications of hydraulic lift tables, manufacturers offer many hydraulic lift table designs. These include, but are not limited to:
- Automotive Lift
- Also known as vehicle lifts or sometimes car or truck lifts, are used to lift vehicles in automotive repair and inspection bays. Automotive lifts are among the strongest hydraulic lift varieties. They not only raise and lower vehicles, such as cars and trucks, they can also lift school buses, dump trucks, and other very large vehicles.
- Post Car Lift
- A variation on the car lift, designed to raise vehicles so that their undersides can be accessed and worked on. They typically feature two upright support columns, four arms attached to a carriage assembly, two hydraulic cylinders, a hydraulic power unit, and a mix of hoses, pulleys, and cables; usually, they’re mounted on a concrete floor.
- Scissor Lift Table
- Perhaps the most common lift variety, raise by means of a crossed, accordion-like base. As the base extends, the platform or basket on top of the scissor lift is elevated to the desired height.
- A scissor lift table is characterized by the scissor-shaped arms beneath it that expand and contract when the table is raised or lowered. The machine uses a motor that exerts hydraulic pressure to raise and lower the unit’s moving scissor arms.
- Mobile Scissor Lift Table
- A scissor lift that, instead of being stationary, is equipped with castors so it can be easily moved as needed. Some models also feature foot pumps and tiltable tables to prevent injuries during the transport of awkward or bulky objects.
- Aerial Lift Table
- Usually a type of scissor lift. They can extend to dramatic heights, typically between ten and fifty feet in the air. This type of hydraulic lift is beneficial for personnel in warehouse buildings requiring access to high shelving units.
- Platform Lift
- Also referred to as elevated work platforms, are conceptually similar to hydraulic lift tables. Platform lifts, however, are much larger than table lifts and are used for larger-scale lifting tasks.
- Pallet Lift
- Used for material handling and shipping applications in which pallets are involved. Also known as transporters, pallet lifts raise pallets from a ground position to a raised position when moving a pallet-loaded object.
- Electric Lifts
- Manufactured in many styles and sizes for a broad range of industrial lifting purposes. Sometimes hydraulic pressure components are integrated into the lift to help give it more power in heavy-duty applications, but the hydraulic system is powered by an electric motor and controlled by a control unit that allows the operator to adjust the lift to the desired height.
- Portable Lifts
- Useful in indoor industrial or commercial settings because it can be wheeled across a flat surface for use in any part of the facility. The most basic portable lifts do not even have a motor at all, just a simple scissor mechanism with a small platform that a person can manually move up and down to the desired height.
- Rotary Lifts
- An Indiana-based company credited with producing the world’s first vehicle lift equipment in 1925. Since then, Rotary Lift products are used in automotive repair contexts throughout the world, and other companies have followed Rotary Lift’s example with their own lines of vehicle lifting products.
Hydraulic Lift Equipment Components
A standard lift table has a wide range of equipment components. These include hydraulic fluid or hydraulic oil, a hydraulic pump, hydraulic valves, a hydraulic roller (used to open and close hydraulic valves), hydraulic cylinders, a drive machine, a rotary joint, and a landing surface for the parts or people being moved.
Tips for Operating Hydraulic Lift Equipment
Each piece of hydraulic equipment is different, but we can offer you a few general tidbits of advice on operating yours.
First, before you turn on your machine, make sure that it is safely set up. If it has castors, make sure they are locked so that the lift won’t move unexpectedly. Check your surroundings for other people, and make sure anyone nearby is aware that you’ll be operating machinery.
Once you’re ready, load the lift, then turn it on. Some lifts turn on with the flip of a switch, while others require you to move a control lever into the unlocked position. If your lift has castors, unlock them and wheel the lift where it needs to go. At this point, you can also raise any safety bars that you have to safely transport your load. After your lift is in place, and any mobile components are locked, either push the foot pump or engage the controls to lift it to the desired height.
Benefits of Using Hydraulic Lifts
There are many reasons to appreciate hydraulic lifts. Among their advantages are cost-effectiveness, longevity, increased worker safety, and efficiency. Additionally, hydraulic lift systems can be used in a variety of lifting operations, including as passenger lifts and supply lifts. Hydraulic lift systems also reduce many manufacturing risks by promoting safe handling practices. By lowering the probability of accidents and time-consuming manual processes, these industrial utilities increase the overall efficiency of a manufacturing facility. By using the most efficient hydraulic lifts at your production facility, you can dramatically increase your returns on production investments.
Design and Customization of Hydraulic Lifts
Since there are several types of hydraulic lifts, hydraulic lift manufacturers have a lot of options during design. For example, hydraulic lift manufacturers make some lifts mobile with attached wheels, much like a forklift, while they design others to be mounted as part of a process line. They also make smaller hydraulic lifts for holding and moving products in manufacturing settings.
When building lifts, manufacturers consider factors such as required strength and durability, size and height restrictions, lifting capacity requirements, and weight capacity requirements. Using these considerations, they decide on design components like material and automation level.
Regardless of a lift’s exact application, though, it will always be constructed from materials that perform well under pressure, like stainless steel, woven wire, or rubber. As for automation level, hydraulic lifts can be fully automated, partially automated, or completely manually operated.
Manufacturers can customize your hydraulic lift equipment in a number of ways. First, they can alter construction so that your equipment has a greater weight capacity. In addition, they can add components like extra arms, foot controls, skirting, and warning lights. They also offer custom color and coating options.
Safety and Compliance Standards for Hydraulic Lifts
When using hydraulic lift systems, it is important to be mindful of threats related to the safety of the equipment and the lives of the workers on the site. Therefore, you must ensure that the lift operators working on your site are well-trained and certified for the job. It would also be a wise decision to send your operators to industry training to help them understand safety hazards. Here are a few safety tips regarding hydraulic lift use:
- Get Certified Equipment
- It is important that the hydraulic equipment you purchase is “up to code.” Of course, while every customer will have a different code or codes to which they need to adhere, there are some general overlaps. These include OSHA standards (in the USA), ISO standards, and, if you’re in Europe, EN or BS EN (British) standards. Make sure to check with your supplier and industry experts to make sure you understand all industry-specific standards as well.
- Hire Trained and Experienced Staff
- Assigning the task of operating a hydraulic lift to certified and experienced operators is key to avoiding mistakes. When hiring operators, make certain that they have considerable industry and job experience. You should also review their technical and professional certifications. Most importantly, ensure that your operators possess working knowledge of the specific type of hydraulic lift being used at your plant. If necessary, send them for technical training. This allows you to minimize potential accidents caused by operator negligence.
- Do Not Abuse Equipment
- To ensure that no accidents occur, hydraulic lift machines and support tools must not be abused. For example, you should never use the hydraulic lift for lifting a load heavier than the lift’s capacity. Taking a lift to extreme levels can negatively affect its inner hydraulic components, including hydraulic cylinders and fuel.
Selecting a Hydraulic Lift System
Before you decide on a specific hydraulic lift system for your process, work with your engineers and other internal resources to document your exact requirements. You should list everything related to your process, such as what the machine will lift, the height it needs to achieve, and how often the machine will perform the operation. You should also have a clear idea of the space where you would be installing the machine. Make sure your plant has sufficient space for running a machine with your specific requirements. Detail this list of considerations before speaking to hydraulic lift manufacturers or suppliers.
Once you have decided which hydraulic lift system is suitable for your needs, find a reliable manufacturer or supplier in your area. You can perform a web search or use a reputable online directory to find a trusted name in the industry. If you find anything negative about a supplier during your research, be sure to review actual customer testimonials and select a supplier with good recognition in the industry. It is important that you select a manufacturer who provides good customer service. After you’ve found a manufacturer you like, check that the supplier offers adequate service options for your business. Explain your requirements to the supplier, and then request that they send the piece of equipment which will best suit your budget and needs.
Hydraulic Lift Terms
- Apron
- Angled, smooth part of landing or car entrance area.
- Cycle
- The complete up and down action of a lift table.
- Cylinder
- A vessel of fluid with a shaft and piston that moves in response to a decrease or increase of pressure.
- Direct Acting Lift
- Lift in which the cylinder is directly attached to the car.
- Drive Machine
- Unit that provides the power and applies the necessary energy to raise and lower a lift.
- Drum
- A cylinder, laid horizontally, used for compaction as part of the winch.
- Elevator
- Used to move equipment or materials from one level to another.
- Ergonomics
- The study of ways to reduce injury and increase ease of physical activity through correct training, posture, and product design.
- Hydraulic
- Moved or operated by pressurized fluid, often through a tube or valve.
- Hydraulic Cylinder
- The combination of a piston and ram, which creates a push and pull force on a part.
- Hydraulic Oil
- A lubricating substance used in hydraulic pistons to create pressure.
- Hydraulic Pump
- A pump that uses flowing water to force a small amount of that water to a pool at another level.
- Jog
- The lowering or raising in short increments of the lift platform.
- Landing
- A surface for work designed with a permanent position for the unloading and loading of lift devices.
- Lifting Capacity
- A rating of a load on a hydraulic lift or scissors lift relative to the application of an evenly distributed load.
- Lift Piston
- Hydraulic cylinder for raising and lowering, usually on a bucket or dozer.
- Outrigger
- Braces used to stabilize equipment through hydraulically controlled means.
- Pitch Cylinder
- Cylinder using hydraulics to control the tilt of a bucket.
- Rotary Joint
- A device that allows the transfer of hydraulic fluid. It is made of two parts: one attached to the operating mechanism and one to the undercarriage of the machine.